River Transportation Definition Geography

This is most common.
River transportation definition geography. The river picks up sediment and carries it downstream in different ways. The definition of a region in. There are four types of transportation. River transport their load by four processes.
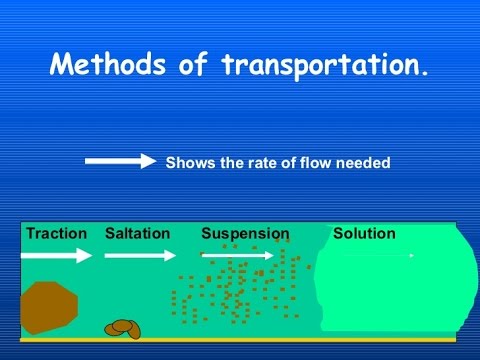
Saltation small pebbles and stones are bounced along the river bed. The energy in a river causes erosion. These materials are called its load. There are three main types of processes that occur in a river.
This typically occurs in areas where the underlying bedrock is limestone. Erosion transportation and deposition all occur in a river. Erosion transportation and deposition the hjulström curve. River transport a type of transportation that moves passengers and cargo primarily by internal waterways both natural including rivers and lakes and man made including canals reservoirs and lock sections on rivers.
These are erosion transportation and deposition. A river carries or transports eroded materials such as mud sand boulders and dissolved materials on its journey. Mainline routes include international routes and are used in. River routes are subdivided into mainline interregional and local.
Today the river continues to serve as a source of irrigation as well as an important transportation and trade route. Traction large heavy pebbles are rolled along the river bed. For thousands of years the river has provided a source of irrigation to transform the dry area around it into lush agricultural land. The nile river flows over 6 600 kilometers 4 100 miles until emptying into the mediterranean sea.
Solution minerals are dissolved in the water and carried along in solution. When energy levels are very high large rocks and boulders can be transported. The definition of a place in geography includes the physical description of the area mountains valleys rivers and the human description roads buildings. Suspension fine light material is carried along in the water.
River transportation a river uses its energy to carry or transport eroded materials such as mud sand boulders and dissolved materials. All three depend on the amount of energy there is in a river.